Unlocking Borders or Complicating Mobility? The Powerful Influence of Regional Economic Communities (RECs) on Nigeria’s Immigration Policy
Introduction
Regional Economic Communities RECS;
Nigeria, as the most populous country in Africa and a significant economic powerhouse, plays a pivotal role in the regional dynamics of West Africa and beyond. Its immigration policies are not just domestic concerns but also integral to the broader frameworks established by various Regional Economic Communities (RECs). These RECs, such as the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), the African Union (AU), and others, have substantial influence on the movement of people, goods, and services across borders. This article delves into the intricate role these RECs play in shaping Nigerian immigration policy, examining their impact, challenges, and the legal frameworks that govern this relationship.
Nigeria, Africa’s most populous nation and one of the continent’s largest economies, occupies a strategic geopolitical and economic position that inevitably shapes and is shaped by its immigration policies. While the movement of persons across borders is as ancient as human civilization, the contemporary realities of international migration have become intricately intertwined with the regulatory frameworks established by sovereign states. In this complex regulatory environment, Regional Economic Communities (RECs) — most notably the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) — have emerged as powerful instruments influencing the direction, scope, and effectiveness of Nigerian immigration policy.
Historically, immigration control and border management were perceived solely as matters of national security, sovereignty, and domestic regulation. However, with globalization, transnational business interests, and the collective ambition for regional integration in Africa, immigration policy has now become a critical intersection of diplomacy, economic strategy, and social development. RECs were created with the noble objective of fostering regional cooperation, economic development, and socio-political stability among member states. Yet, their influence on national immigration frameworks, particularly in Nigeria, is both facilitative and, at times, contentious.
The ECOWAS Protocol on Free Movement of Persons, Residence, and Establishment is the most significant REC-related instrument impacting Nigerian immigration law. Adopted in 1979, this protocol guarantees citizens of member states the right to enter, reside, and establish businesses in any other member country without the stringent visa and work permit requirements traditionally associated with cross-border migration.
For Nigeria, a country that shares extensive land borders with Benin, Niger, Chad, and Cameroon, and which serves as the economic hub of West Africa, the implications of such open-border policies are profound. On one hand, these frameworks promote intra-African mobility, regional trade, and socio-economic integration. On the other, they complicate internal security measures, labor market regulation, and the capacity to control illegal migration and transnational crime.
The Nigerian government, through its Immigration Act of 2015 and various executive policies, has attempted to harmonize its national interests with its regional commitments. Yet, the task remains daunting. The open-border ambition of the ECOWAS framework, while laudable, has been fraught with practical challenges including porous borders, human trafficking, smuggling of goods, and security threats from terrorist networks like Boko Haram and banditry groups operating across the Sahel.
More critically, the role of RECs in shaping Nigerian immigration policy raises questions about the balance between national sovereignty and regional solidarity. How much control should a sovereign state relinquish in pursuit of regional unity? Can Nigeria effectively regulate its labor market when migration flows are dictated by regional treaties that often lack effective enforcement mechanisms? These questions highlight the inherent tension between policy ideals and operational realities on the ground.
It is also important to recognize the socio-economic advantages that RECs bring to the table. Nigerian citizens benefit from the same rights to reside and work in other ECOWAS countries, enabling labor mobility, business expansion, and cultural exchange. For a country with a significant youthful population and rising unemployment rates, these migration channels can serve as valuable pressure valves. Furthermore, cross-border migration supported by RECs fosters remittances, cross-cultural marriages, and the sharing of skills and expertise, all of which are important for the broader socio-economic landscape of Nigeria.
Despite these advantages, there remains an ongoing debate within policymaking circles about whether the benefits of REC-induced migration outweigh the burdens. Critics argue that Nigeria bears the brunt of migration inflows from less stable ECOWAS nations, creating strain on infrastructure, healthcare, housing, and social services in major urban centers like Lagos and Abuja. The country’s relative economic attractiveness has turned it into a migration magnet within the West African sub-region.
Nigeria’s response has been cautious. While remaining committed to its ECOWAS obligations, Nigerian authorities have periodically closed land borders or tightened immigration controls to curb smuggling, illegal migration, and cross-border crime. Such actions have occasionally put Nigeria at odds with its REC partners, raising diplomatic concerns and challenging the spirit of regional integration.
The effectiveness of RECs in shaping Nigerian immigration policy is therefore neither purely positive nor wholly negative. It is a complex dance of compromise, negotiation, and strategic alignment. Nigeria stands at the crossroads of upholding its sovereign right to control its borders while championing the pan-African dream of unity and integration.
In examining the role of RECs in Nigerian immigration policy, this discourse seeks to explore whether these regional mechanisms truly facilitate sustainable development and mutual prosperity or whether they inadvertently enable systemic vulnerabilities that undermine national security and socio-economic planning. Through a deeper understanding of this dynamic relationship, policymakers, legal practitioners, investors, and the general public can better appreciate the challenges and opportunities that lie within Nigeria’s immigration framework as influenced by the regional economic architecture of the African continent.
The Concept of Regional Economic Communities (RECs)
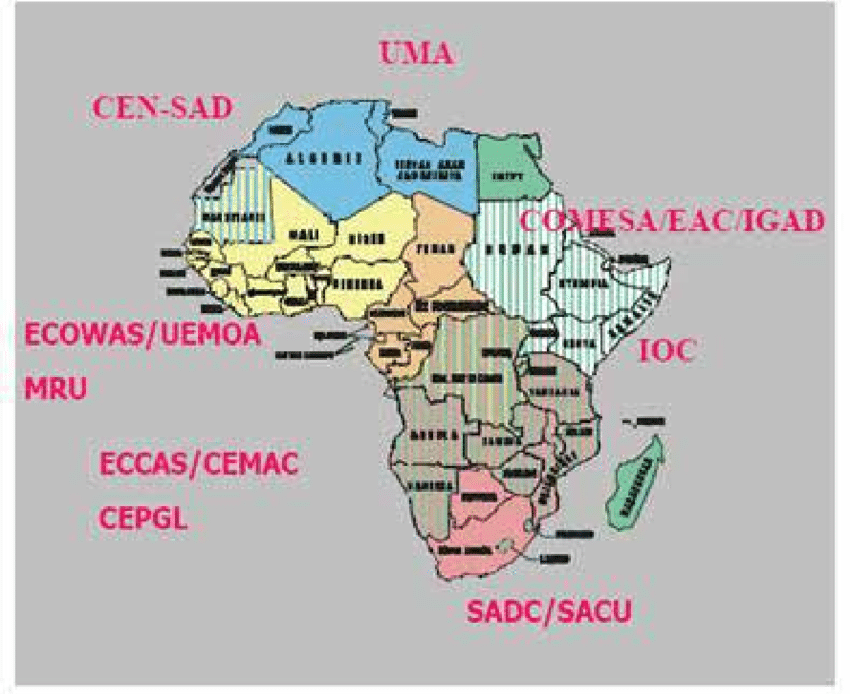
Regional Economic Communities (RECs) are regional groupings of African states with the purpose of achieving greater economic integration, fostering development, and facilitating trade and investment. There are eight RECs recognized by the African Union: ECOWAS, the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the Common Market for Eastern and
Southern Africa (COMESA), the East African Community (EAC), the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), the Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD), the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS), and the Arab Maghreb Union (UMA). These organizations aim to promote regional cooperation and integration, which, in turn, influences immigration policies among member states.
Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
Established in 1975, ECOWAS is perhaps the most influential REC affecting Nigeria’s immigration policy. ECOWAS was created with the objective of promoting economic integration and cooperation among its 15 member states. One of its primary tenets is the facilitation of free movement of persons, goods, and services, which has significant implications for immigration policies in Nigeria.
ECOWAS Protocol on Free Movement
The ECOWAS Protocol on Free Movement of Persons, Residence, and Establishment is a cornerstone document that outlines the right of citizens of member states to enter, reside, and establish in any ECOWAS country. This protocol is instrumental in shaping Nigeria’s immigration policy. It mandates that:
- Right of Entry and Abolition of Visa: ECOWAS citizens are entitled to enter any member state without a visa for up to 90 days.
- Right of Residence: Citizens can apply for residency and are granted the right to reside in member states.
- Right of Establishment: Citizens have the right to establish businesses and engage in economic activities under the same conditions as nationals of the host country.
This protocol necessitates Nigeria to align its immigration policies to facilitate these rights, impacting visa regulations, residency permits, and business establishment procedures.
African Union (AU)
The African Union, established in 2001, replaced the Organization of African Unity (OAU) and aims to promote political and economic integration across the continent. While the AU encompasses all African states, its policies and treaties often intersect with those of RECs, influencing national policies, including immigration.
The AU Agenda 2063
The AU Agenda 2063 is a strategic framework for the socio-economic transformation of Africa over the next 50 years. One of its aspirations is to achieve “an integrated continent, politically united and based on the ideals of Pan-Africanism and the vision of Africa’s Renaissance.” This includes the free movement of people across the continent. In alignment with this agenda, Nigeria’s immigration policies are expected to facilitate easier movement for citizens of AU member states, influencing visa policies and residency requirements.
Other Regional Economic Communities
Other RECs, such as the SADC and COMESA, though not directly impacting Nigeria, contribute to the broader continental integration efforts which indirectly influence Nigeria’s stance on immigration policies. As Nigeria engages in inter-regional trade and cooperation, the principles adopted by these RECs can have a ripple effect, encouraging harmonization of immigration policies across the continent.
Impact of RECs on Nigerian Immigration Policy
The influence of RECs on Nigerian immigration policy can be seen through various legislative and policy measures that the country has adopted. This section explores how these regional frameworks have been integrated into Nigeria’s national policies and the resulting impact.
Legislative Framework
Nigeria’s legislative framework governing immigration is influenced by its commitments to RECs, particularly ECOWAS. Key legislations include:
- Immigration Act 2015: This Act provides the legal basis for regulating immigration in Nigeria. It includes provisions that align with ECOWAS protocols, such as visa-free entry for ECOWAS citizens and regulations on residency and work permits.
- Immigration Regulations 2017: These regulations complement the Immigration Act and provide detailed guidelines on the implementation of immigration policies. They incorporate REC protocols, ensuring that Nigeria’s immigration policies are in harmony with regional commitments.
Policy Measures
Beyond legislation, Nigeria has implemented various policy measures to facilitate regional integration:
- Visa-Free Entry: In compliance with the ECOWAS protocol, Nigeria grants visa-free entry to citizens of ECOWAS member states for up to 90 days. This policy has significantly increased the movement of people within the region, fostering economic and social ties.
- Residency and Work Permits: Nigeria has streamlined the process for obtaining residency and work permits for ECOWAS citizens, making it easier for them to live and work in the country. This policy aims to attract skilled labor and promote economic integration.
- Border Management: To facilitate free movement while ensuring security, Nigeria has adopted advanced border management systems. This includes biometric data collection and the use of electronic gates at border crossings, which help monitor and regulate the flow of people in line with REC protocols.
Economic and Social Impact
The alignment of Nigerian immigration policy with REC frameworks has had several economic and social impacts:
- Economic Growth: The free movement of people has facilitated trade and investment, contributing to economic growth. Businesses benefit from a larger market, and labor mobility helps address skill shortages in various sectors.
- Cultural Exchange: Increased movement of people has fostered cultural exchange and social cohesion within the region. It has allowed for a greater understanding and appreciation of diverse cultures, promoting regional unity.
- Challenges: Despite the benefits, there are challenges, such as the strain on public services and infrastructure due to increased migration, and concerns about security and illegal immigration.
Challenges and Obstacles
While the integration of REC protocols into Nigerian immigration policy has been largely beneficial, it is not without challenges. These obstacles hinder the seamless implementation of regional frameworks and require attention to ensure the successful realization of REC objectives.
1. Inconsistent Implementation
One of the significant challenges is the inconsistent implementation of REC protocols among member states. While Nigeria may adhere to ECOWAS protocols, other member states may not fully comply, leading to disparities and confusion. This inconsistency can undermine the objectives of regional integration and create barriers for citizens seeking to move across borders.
2. Security Concerns
The facilitation of free movement poses security challenges, particularly in the context of terrorism and organized crime. Nigeria has faced significant security threats from groups such as Boko Haram, and the porous borders resulting from free movement protocols can exacerbate these issues. Balancing the need for security with the commitment to free movement is a delicate task for Nigerian authorities.
3. Economic Disparities
Economic disparities among member states can lead to imbalanced migration flows. Countries with stronger economies, like Nigeria, may attract more migrants, leading to potential strains on resources and infrastructure. This can create tensions and resistance to the full implementation of free movement protocols.
4. Public Perception and Xenophobia
Public perception and xenophobia can also pose obstacles. There may be resistance from local populations who perceive migrants as competitors for jobs and public services. Addressing these sentiments requires public awareness campaigns and policies that promote social inclusion and harmony.
Legal Frameworks and Judicial Interpretation
The role of the judiciary in interpreting and enforcing immigration laws and REC protocols is crucial. Nigerian courts have a significant role in ensuring that immigration policies comply with regional commitments and uphold the rights of migrants.
Judicial Review
Judicial review plays a vital role in ensuring that immigration policies are implemented fairly and in compliance with regional protocols. Courts have the authority to review administrative decisions and actions to ensure they align with Nigeria’s obligations under REC agreements. This provides a mechanism for accountability and protection of migrants’ rights.
Future Prospects and Recommendations
The future of Nigerian immigration policy in the context of RECs is promising but requires strategic actions to address existing challenges and fully harness the benefits of regional integration.
Strengthening Regional Cooperation
To overcome inconsistencies in implementation, there is a need for stronger regional cooperation and coordination among member states. Nigeria should work closely with other ECOWAS members to ensure uniform application of protocols and share best practices for managing migration.
Enhancing Security Measures
Balancing free movement with security concerns requires advanced measures. Nigeria should invest in modern border management technologies and collaborate with regional security agencies to monitor and address security threats effectively.
Promoting Economic Development
Addressing economic disparities within the region can help balance migration flows. Nigeria should support regional economic development initiatives and invest in infrastructure and public services to accommodate increased migration.
Public Awareness and Inclusion
Public awareness campaigns are essential to mitigate xenophobia and promote social inclusion. The Nigerian government, in collaboration with civil society and international organizations, should undertake initiatives to educate the public about the benefits of regional integration and the rights of migrants. Promoting stories of successful integration and contributions by migrants to the economy can help foster a more welcoming environment.
Strengthening Legal Frameworks
Enhancing the legal frameworks to align more closely with REC protocols is critical. This includes regular updates to immigration laws and regulations to reflect evolving regional agreements and best practices. Ensuring that these laws are effectively enforced and that there are clear mechanisms for redress in case of violations is equally important.
Capacity Building
Building the capacity of immigration officials and border management personnel is vital. Training programs on REC protocols, human rights, and modern immigration practices can help ensure that officials are well-equipped to handle the complexities of regional integration.
Enhancing Judicial Oversight
Strengthening the role of the judiciary in overseeing the implementation of immigration policies can ensure greater compliance with REC protocols. This includes training judges on regional agreements and human rights law, and establishing specialized tribunals or courts to handle immigration-related cases more efficiently.
Collaboration with International Organizations
Collaboration with international organizations such as the International Organization for Migration (IOM) and the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) can provide technical assistance, funding, and expertise to support Nigeria’s immigration policies. These organizations can also help in addressing broader issues such as human trafficking and the protection of vulnerable migrants.
Conclusion
The role of Regional Economic Communities (RECs) in shaping Nigerian immigration policy is profound and multifaceted. Through frameworks established by ECOWAS, the AU, and other regional bodies, Nigeria has made significant strides in promoting the free movement of people, goods, and services. However, the journey towards full regional integration is fraught with challenges, including inconsistent implementation, security concerns, economic disparities, and public perception issues.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that includes strengthening regional cooperation, enhancing security measures, promoting economic development, and fostering public awareness and inclusion. Additionally, robust legal frameworks, capacity building for officials, and active judicial oversight are essential components in ensuring that Nigeria’s immigration policies align with its regional commitments.
The future of Nigeria’s immigration policy, influenced by its participation in RECs, holds great promise for fostering economic growth, social cohesion, and regional stability. By addressing the existing obstacles and leveraging the benefits of regional integration, Nigeria can continue to play a pivotal role in the development and prosperity of the West African region and the African continent as a whole.
In reflecting upon the role of Regional Economic Communities (RECs) in shaping Nigerian immigration policy, it becomes evident that these regional institutions wield both constructive influence and unintended disruption. The pursuit of regional integration, economic cooperation, and free movement of persons, as embodied by the ECOWAS protocols and similar initiatives across Africa, represents an ambitious vision of collective prosperity, mutual development, and continental solidarity. However, the Nigerian experience has exposed critical fissures in the implementation and governance of these ideals, revealing the delicate balance between aspiration and practicality.
Nigeria’s geographic size, population strength, and economic potential make it an inevitable focal point for West African migration flows. The country’s regional dominance and its role as the de facto economic powerhouse of ECOWAS attract not only legitimate labor migrants and businesspeople but also illicit networks seeking to exploit border vulnerabilities. While the ECOWAS Free Movement Protocol promises freedom, dignity, and opportunity for citizens of the region, the operational realities at Nigeria’s borders and within its domestic spaces often tell a different story — one marked by abuse of such freedoms, border insecurity, and inadequate enforcement of migration standards.
From a legal and policy perspective, the Nigerian government continues to grapple with the contradictions between its regional commitments and its national interests. Immigration laws, including the Immigration Act of 2015 and the Nigeria Immigration Regulations of 2017, attempt to assert control, maintain order, and protect national security while remaining aligned with ECOWAS treaties. Yet, enforcement mechanisms across the sub-region are inconsistent, and border patrol capacities are frequently overwhelmed.
One of the most pressing consequences of REC-driven migration is the strain it places on Nigeria’s urban centers, labor market, and social infrastructure. Lagos, Abuja, Kano, and other major cities are already battling with high unemployment, housing deficits, and stretched healthcare systems. The unregulated influx of migrants from neighboring countries — often driven by economic desperation, political instability, or environmental crises — compounds these domestic challenges. While the free movement policy facilitates economic opportunity for many, it also creates avenues for human trafficking, illegal arms trade, and the unchecked movement of extremist elements.
The Nigerian government’s periodic resort to border closures, as witnessed between 2019 and 2021, is symptomatic of the tension between regional ideals and national priorities. While such measures temporarily curb illegal activities, they also provoke diplomatic friction and threaten the spirit of African unity that RECs aspire to uphold. These actions expose a fundamental flaw within the REC framework: the lack of harmonized border management systems, shared intelligence networks, and joint enforcement strategies among member states.
Nonetheless, it would be reductionist to focus solely on the challenges without acknowledging the significant benefits that Nigeria derives from regional economic cooperation. The facilitation of cross-border trade, cultural exchange, professional mobility, and investment opportunities across ECOWAS remains a vital pillar of Nigeria’s foreign policy. Many Nigerian entrepreneurs, artisans, and professionals have expanded their ventures across the region, leveraging the legal right to establish businesses and reside freely in member states. The remittance flows from Nigerians living in other ECOWAS countries contribute meaningfully to the national economy, strengthening household incomes and driving local development projects.
Moreover, the collective bargaining power offered by RECs in negotiations with external partners, such as the European Union and other global powers, positions Nigeria advantageously within global migration dialogues and trade discussions. It underscores the fact that regional integration is not merely about the movement of people but also about strategic positioning in the global economic system.
However, to optimize the role of RECs in Nigerian immigration policy, deliberate reforms are needed. First, there must be robust coordination between national immigration authorities and REC institutions to strengthen monitoring, data collection, and enforcement. Border management must evolve from manual, ad hoc practices to technology-driven systems supported by biometric identification, electronic visa processing, and shared digital platforms among member states.
Secondly, Nigeria and other REC members must invest in joint security architecture — intelligence-sharing, joint task forces, and synchronized law enforcement responses to cross-border threats. The current fragmentation in enforcement creates loopholes that criminal elements readily exploit.
Thirdly, there must be a strategic recalibration of REC protocols to address contemporary realities. The free movement agreements should not be static relics of the past but living instruments, periodically reviewed and restructured to reflect emerging socio-economic dynamics, security challenges, and global migration patterns.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of RECs in shaping Nigerian immigration policy hinges on political will, institutional capacity, and mutual respect among member states. Nigeria’s leadership role in ECOWAS places it at the forefront of this conversation, with the responsibility to steer the dialogue toward reforms that balance national security with regional aspirations.
In conclusion, while Regional Economic Communities (RECs) remain indispensable in Nigeria’s quest for regional integration and development, their influence on immigration policy presents a double-edged sword — offering both opportunity and risk. To navigate this complex landscape successfully, Nigeria must adopt a pragmatic, security-conscious, and economically sound approach that honors its regional obligations without sacrificing its national interest. Only through such strategic alignment can Nigeria harness the full potential of RECs while safeguarding its borders, its people, and its sovereignty.
Contact Us
For premier ways of the Role of Regional Economic Communities (RECs) in Nigerian Immigration Policy, contact Chaman Law Firm today. Our offices are conveniently located in Lagos, FCT Abuja, Ogun State, and the UK. We are readily available to assist you with your legal needs. Whether you require consultation, representation, or ongoing legal support, Chaman Law Firm is your trusted partner in the Role of Regional Economic Communities (RECs) in Nigerian Immigration Policy.
Call us at 08065553671 or email us at info@chamanlawfirm.com to schedule a consultation.
- Role of Regional Economic Communities in Nigeria
- RECs and Nigerian immigration policy
- ECOWAS free movement Nigeria
- Nigerian border management REC
- Immigration policy Nigeria ECOWAS
- Regional integration and Nigerian immigration
- Free movement of persons in West Africa
- RECs and Nigerian migration
- ECOWAS Protocol on Free Movement
- Regional Economic Communities and Nigeria
Chaman Law Firm: Your Trusted Legal Partner in the Role of Regional Economic Communities (RECs) in Nigerian Immigration Policy
By choosing Chaman Law Firm, you are selecting a team of dedicated professionals committed to providing exceptional immigration legal services tailored to your unique needs. Let us be your advocate and guide in the complex world of the Role of Regional Economic Communities (RECs) in Nigerian Immigration Policy, ensuring your interests are protected and your goals are achieved.