
In the fast-paced and complex world of construction, disputes are an inevitable part of project management. In Nigeria, where the construction industry is rapidly evolving amidst unique regulatory, economic, and environmental challenges, managing contractual disputes effectively is crucial for project success. This article provides an in-depth exploration of strategies and best practices for managing contractual disputes in Nigerian construction contracts, emphasizing the importance of proactive measures, legal frameworks, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Understanding Contractual Disputes in Nigerian Construction Projects
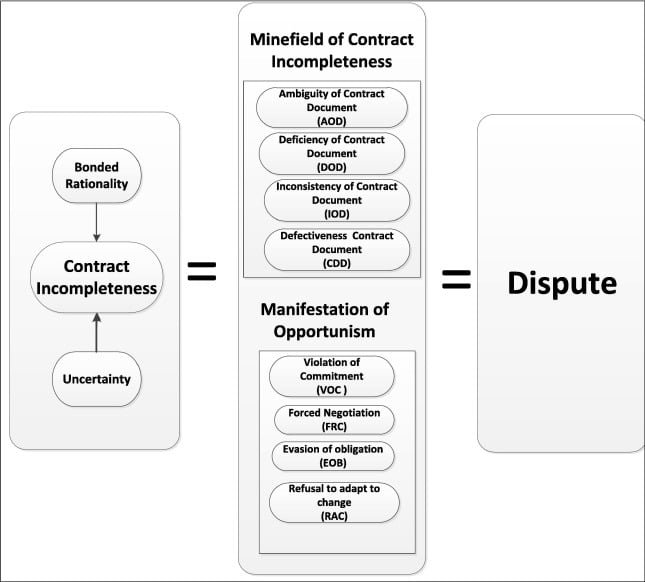
Contractual disputes in Nigerian construction projects often arise from various factors, including project delays, cost overruns, contractual breaches, and disagreements over contract terms. These disputes can have significant repercussions on project timelines, costs, and relationships between stakeholders. Effective management of these disputes is essential to ensure that projects are completed on time, within budget, and in compliance with contractual obligations.
Key Causes of Contractual Disputes in Nigerian Construction Contracts
1. Ambiguity in Contract Terms: Ambiguous or poorly defined contract terms can lead to misunderstandings and disagreements between parties. In Nigerian construction contracts, this often involves unclear specifications, scope of work, or payment terms.
2. Delays and Extensions of Time: Delays in construction work, whether due to weather conditions, supply chain issues, or other unforeseen factors, can lead to disputes over extensions of time and associated costs.
3. Cost Overruns: Disputes frequently arise from cost overruns, which can result from changes in project scope, unforeseen site conditions, or variations in material costs.
4. Quality of Work: Disagreements over the quality of work and adherence to specified standards and specifications can lead to disputes, especially when parties have differing interpretations of contract requirements.
5. Contractual Breaches: Breaches of contract, whether due to non-performance, delayed performance, or failure to meet contractual obligations, are a common source of disputes in construction projects.
Best Practices for Managing Contractual Disputes
1. Clear and Detailed Contract Drafting
Define Scope and Specifications: Ensure that the contract clearly defines the scope of work, project specifications, and performance standards. Avoid ambiguous language and ensure that all parties have a clear understanding of their obligations.
Include Dispute Resolution Clauses: Incorporate comprehensive dispute resolution clauses that outline the procedures for addressing disputes, including negotiation, mediation, arbitration, or litigation. Specify the methods and timelines for resolving disputes to avoid delays and confusion.
Detail Payment Terms: Clearly outline payment terms, including schedules, milestones, and conditions for variations or additional work. This reduces the likelihood of disputes related to payments and financial arrangements.
2. Effective Communication and Documentation
Regular Communication: Maintain open and regular communication between all parties involved in the project. Address issues and potential disputes early through discussions and meetings to prevent escalation.
Detailed Record-Keeping: Keep thorough records of all project activities, including correspondence, meeting minutes, change orders, and progress reports. These records serve as crucial evidence in resolving disputes and clarifying contractual obligations.
Document Changes and Variations: Ensure that any changes to the contract or scope of work are documented and agreed upon by all parties. Use formal change orders or amendments to capture these changes and their impact on the contract.
3. Proactive Risk Management
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Conduct a thorough risk assessment at the outset of the project to identify potential sources of disputes. Develop and implement risk mitigation strategies to address these risks proactively.
Contingency Planning: Establish contingency plans for handling potential disputes or issues that may arise during the project. Having predefined procedures in place can streamline the dispute resolution process and minimize disruptions.
4. Engage Legal and Industry Experts
Consult Legal Professionals: Engage legal professionals with expertise in Nigerian construction law to review contracts, provide advice, and assist in dispute resolution. Their knowledge of local regulations and legal precedents can be invaluable in managing disputes.
Involve Industry Experts: In cases involving technical disputes or disagreements over construction practices, involve industry experts or consultants who can provide objective assessments and recommendations.
5. Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) Mechanisms
Negotiation: Attempt to resolve disputes through direct negotiation between the parties. Negotiation allows for flexible and amicable solutions without resorting to formal proceedings.
Mediation: Utilize mediation as a formal process in which a neutral third party facilitates discussions and helps the parties reach a mutually acceptable resolution. Mediation can be a cost-effective and efficient alternative to litigation.
Arbitration: Consider arbitration for more formal dispute resolution. Arbitration involves a neutral arbitrator or panel who makes a binding decision based on the evidence presented. Ensure that the arbitration process is clearly defined in the contract.
6. Litigation as a Last Resort
Understand the Litigation Process: If disputes cannot be resolved through negotiation, mediation, or arbitration, litigation may be necessary. Familiarize yourself with the Nigerian court system, procedural requirements, and potential outcomes.
Prepare for Litigation: Ensure that you have comprehensive documentation and evidence to support your case in court. Engage experienced legal counsel to represent your interests and navigate the litigation process effectively.
Legal Framework Governing Construction Contracts in Nigeria
1. Contract Law
Contract Act: The Nigerian Contract Act governs the formation, performance, and enforcement of contracts. It provides the legal basis for resolving disputes arising from contractual breaches or disagreements.
Common Law Principles: Nigerian contract law is influenced by common law principles, which guide the interpretation of contract terms, performance obligations, and remedies for breaches.
2. Construction Industry Regulations
Federal and State Regulations: Compliance with federal and state regulations governing construction practices, safety standards, and environmental requirements is essential. Ensure that your contracts reflect these regulations to avoid legal challenges.
Building Codes and Standards: Adherence to building codes and industry standards is crucial for maintaining quality and safety. Incorporate relevant codes and standards into your contracts to ensure compliance.
3. Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Arbitration and Mediation Institutions: The Nigerian Arbitration and Conciliation Act provides a framework for arbitration and mediation. Institutions such as the Nigerian Arbitration Association and the Lagos Court of Arbitration offer resources and support for resolving disputes.
Judicial Precedents: Nigerian courts have established precedents in construction dispute cases. Familiarize yourself with relevant case law to understand how courts interpret and enforce contract terms.
Conclusion
Managing contractual disputes in Nigerian construction contracts requires a strategic and proactive approach. By focusing on clear contract drafting, effective communication, proactive risk management, and appropriate dispute resolution mechanisms, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of construction disputes and achieve successful project outcomes. Understanding the legal framework governing construction contracts and engaging with legal and industry experts further enhances the ability to manage and resolve disputes effectively. In Nigeria’s rapidly evolving construction sector, mastering these strategies is essential for maintaining project integrity, minimizing disruptions, and fostering positive relationships between all parties involved.
· Contractual Disputes
· Construction Contracts
· Risk Management
· Dispute Resolution
· Contract Drafting
· Ambiguity in Contracts
· Arbitration
· Mediation
· Negotiation
· Litigation
· Payment Terms
· Delay Claims
· Nigerian Contract Law
· Federal Regulations
· Building Codes and Standards
Contact Us
Chaman Law Firm today. Our offices are conveniently located in Lagos, FCT Abuja, Ogun State, and the UK. We are readily available to assist you with your legal needs. Whether you require consultation, representation, or ongoing legal support, Chaman Law Firm is your trusted partner.
Call us at 08065553671 or email us at info@chamanlawfirm.com to schedule a consultation.

