The advent of autonomous vehicles (AVs) has sparked a revolution in the global automotive industry, promising safer roads, reduced traffic congestion, and enhanced mobility. However, the integration of these self-driving cars into Nigeria’s traffic ecosystem presents unique legal challenges that necessitate a comprehensive review of the country’s traffic laws. This article delves into the legal implications of autonomous vehicles in Nigerian traffic laws, exploring the areas that require regulatory attention to ensure the safe and effective deployment of this transformative technology.
Understanding Autonomous Vehicles
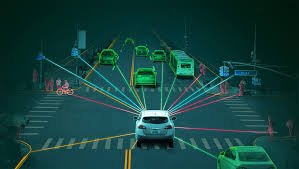
Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars, are equipped with advanced sensors, machine learning algorithms, and artificial intelligence systems that allow them to navigate and operate without human intervention. These vehicles rely on a combination of cameras, radar, LIDAR, and GPS to perceive their environment, make decisions, and drive to a destination with minimal or no human input. The deployment of AVs in Nigeria raises questions about liability, safety standards, data privacy, and the adequacy of existing traffic laws.
The Current State of Nigerian Traffic Laws
Nigeria’s traffic laws, as encapsulated in the Federal Road Safety Commission (FRSC) Act, the Nigerian Highway Code, and the Lagos State Traffic Law, were developed with traditional human-driven vehicles in mind. These laws emphasize the responsibilities of drivers, vehicle registration, road safety regulations, and penalties for traffic violations. However, the introduction of autonomous vehicles necessitates a reevaluation of these laws, as they do not currently address the unique aspects of self-driving technology.
Legal Implications of Autonomous Vehicles
. Liability and Accountability
One of the most significant legal implications of autonomous vehicles in Nigerian traffic laws is the issue of liability. In the event of an accident involving an AV, determining who is at fault can be complex. Traditional traffic laws place responsibility on the driver, but in the case of AVs, the “driver” may be a software program or an AI system. This raises questions about whether liability should fall on the manufacturer, the software developer, the owner of the vehicle, or a combination of these parties. Nigerian traffic laws will need to establish clear guidelines on liability in accidents involving AVs to protect the rights of all parties involved.
- Safety Standards and Compliance
Autonomous vehicles operate using sophisticated technology that requires rigorous safety standards to prevent malfunctions or accidents. Nigerian traffic laws currently outline safety standards for human-driven vehicles, but these regulations may not adequately cover the technological intricacies of AVs. The Nigerian government will need to develop new safety standards specifically tailored to autonomous vehicles, ensuring that they meet the necessary criteria for safe operation on Nigerian roads. This may involve regular software updates, system checks, and compliance with international AV safety protocols.
- Data Privacy and Cybersecurity
The operation of autonomous vehicles relies heavily on data collection, processing, and sharing. AVs gather vast amounts of data from their surroundings, including information about other vehicles, road conditions, and pedestrian movements. This data is critical for the safe operation of the vehicle, but it also raises concerns about privacy and cybersecurity. Nigerian traffic laws will need to address the protection of personal data collected by AVs and establish protocols for cybersecurity to prevent hacking or unauthorized access to the vehicle’s systems. Ensuring data privacy and cybersecurity in the context of AVs is essential to maintaining public trust and safety.
- Insurance Policies
The introduction of autonomous vehicles also has implications for the insurance industry in Nigeria. Traditional car insurance policies are based on the assumption that a human driver is responsible for the vehicle’s operation. However, with AVs, the risk profile changes, as accidents may result from software errors or system failures rather than human error. Nigerian insurance companies will need to develop new insurance products tailored to the specific risks associated with autonomous vehicles. These policies should consider the shared responsibility between manufacturers, software developers, and vehicle owners.
- Traffic Law Enforcement
Enforcing traffic laws with autonomous vehicles presents unique challenges. AVs are programmed to follow traffic rules, but they may encounter situations where human drivers make unpredictable decisions, leading to potential conflicts. Nigerian traffic law enforcement agencies, such as the FRSC, will need to adapt their strategies to accommodate the presence of AVs on the roads. This may involve the use of new technologies, such as vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication systems, to monitor and manage traffic flow effectively.
- Ethical Considerations
Autonomous vehicles operate based on algorithms that make decisions in real-time. In certain scenarios, AVs may face ethical dilemmas, such as choosing between two unfavorable outcomes in an unavoidable accident. Nigerian traffic laws will need to consider the ethical implications of such decisions and establish guidelines for how AVs should be programmed to handle these situations. Ensuring that AVs adhere to ethical standards is crucial for public acceptance and trust in the technology.
The Path Forward
To fully integrate autonomous vehicles into Nigeria’s transportation system, a comprehensive legal and regulatory framework must be developed. This framework should address the unique challenges posed by AVs while ensuring the safety, security, and rights of all road users. Collaboration between government agencies, the automotive industry, technology companies, and legal experts will be essential in crafting traffic laws that are fit for the era of autonomous vehicles.
Conclusion
The arrival of autonomous vehicles in Nigeria heralds a new chapter in the country’s transportation history. However, it also presents significant legal implications that must be carefully considered and addressed. By updating Nigerian traffic laws to accommodate the complexities of AV technology, the country can ensure a smooth transition to a future where self-driving cars are an integral part of the transportation landscape. This proactive approach will not only enhance road safety but also position Nigeria as a leader in embracing innovative automotive technologies.
· Autonomous Vehicles (AVs)
· Self-Driving Cars
· Liability in Autonomous Vehicles
· Nigerian Traffic Laws
· Federal Road Safety Commission (FRSC)
· Safety Standards for AVs
· Data Privacy
· Cybersecurity in Autonomous Vehicles
· Insurance for Autonomous Vehicles
· Traffic Law Enforcement
· Ethical Considerations in AVs
· Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) Communication
Contact Us
Chaman Law Firm today. Our offices are conveniently located in Lagos, FCT Abuja, Ogun State, and the UK. We are readily available to assist you with your legal needs. Whether you require consultation, representation, or ongoing legal support, Chaman Law Firm is your trusted partner.
Call us at 08065553671 or email us at info@chamanlawfirm.com to schedule a consultation.

