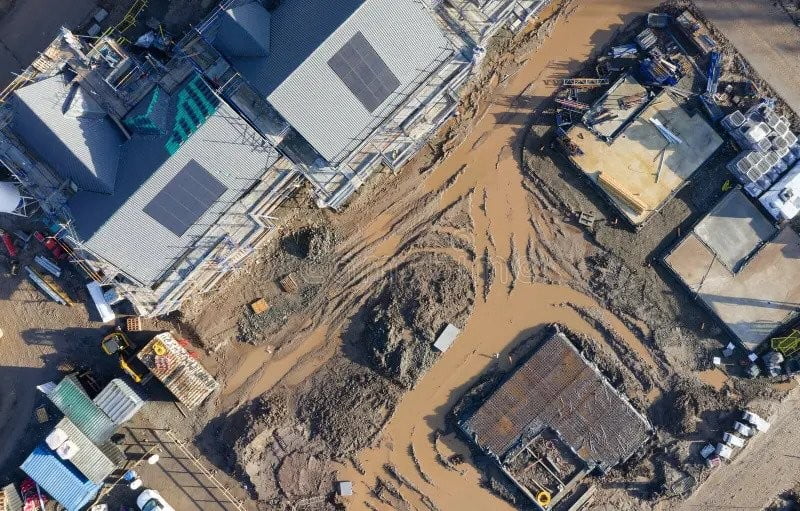
Urban redevelopment is a critical process for modernizing and revitalizing cities, addressing infrastructure deficits, and enhancing the quality of life for residents. In Nigeria, a country experiencing rapid urban growth and economic transformation, urban redevelopment projects are both essential and challenging. This article explores the multifaceted challenges of urban redevelopment projects in Nigeria, emphasizing how these issues impact the effectiveness and sustainability of redevelopment efforts.
Understanding Urban Redevelopment in Nigeria
Urban redevelopment involves the renovation, reorganization, or complete reconstruction of urban areas to improve their functionality, aesthetics, and economic viability. In Nigeria, such projects are crucial due to the country’s fast-paced urbanization and the growing demand for housing, commercial spaces, and infrastructure. Redevelopment projects often aim to address issues such as inadequate housing, poor infrastructure, and environmental degradation, while also fostering economic development and social cohesion.
Major Challenges of Urban Redevelopment Projects in Nigeria
1. Inadequate Infrastructure and Poor Urban Planning
One of the primary challenges of urban redevelopment in Nigeria is the lack of adequate infrastructure and poor urban planning. Many Nigerian cities suffer from outdated infrastructure, including roads, sewage systems, and public utilities. Redevelopment projects often face difficulties integrating new developments with existing infrastructure that is not designed to support modern urban demands. Additionally, poor urban planning practices, characterized by haphazard growth and insufficient zoning regulations, further complicate redevelopment efforts.
2. Land Ownership and Title Disputes
Land ownership issues and title disputes are significant barriers to urban redevelopment in Nigeria. The complex land tenure system, which includes customary land ownership and informal land markets, often leads to disputes over land titles and boundaries. Redevelopment projects can be stalled or derailed by conflicting claims and legal uncertainties regarding land ownership. Resolving these disputes requires careful negotiation and legal intervention, which can delay projects and increase costs.
3. Corruption and Bureaucracy
Corruption and bureaucratic inefficiencies pose major challenges to urban redevelopment projects in Nigeria. Corruption can lead to misallocation of resources, inflated project costs, and delays in obtaining necessary permits and approvals. Bureaucratic red tape, including cumbersome administrative procedures and slow decision-making processes, can also hinder the progress of redevelopment projects. Addressing these issues requires reforms to improve transparency and streamline regulatory processes.
4. Funding and Financial Constraints
Securing adequate funding for urban redevelopment projects is a persistent challenge in Nigeria. Many redevelopment initiatives require substantial financial investment, which can be difficult to obtain due to limited access to capital and financial instability. Government budgets for infrastructure and urban development are often constrained, and private investors may be wary of the risks associated with redevelopment projects. Creative financing solutions, such as public-private partnerships (PPPs) and innovative funding mechanisms, are essential to overcoming these financial constraints.
5. Social Displacement and Community Resistance
Urban redevelopment projects can lead to social displacement and resistance from local communities. Redevelopment often involves the relocation of residents and businesses, which can disrupt established communities and lead to the loss of social networks. Communities may resist redevelopment efforts if they perceive that the benefits do not outweigh the costs or if they feel excluded from the planning process. Engaging with communities, addressing their concerns, and providing adequate compensation and support are crucial for minimizing social disruption.
6. Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
Environmental sustainability is a critical issue in urban redevelopment projects. In Nigeria, rapid urbanization has led to environmental challenges such as deforestation, pollution, and inadequate waste management. Redevelopment projects must consider the environmental impact of construction activities and incorporate sustainable practices to mitigate negative effects. This includes integrating green building technologies, improving waste management systems, and protecting natural resources.
7. Lack of Technical Expertise and Capacity
The successful implementation of urban redevelopment projects requires technical expertise and capacity, which may be lacking in Nigeria. Many redevelopment projects involve complex engineering, architectural, and urban planning tasks that require specialized skills and knowledge. The shortage of qualified professionals and limited technical capacity can hinder the quality and efficiency of redevelopment efforts. Investing in training and capacity-building initiatives is essential to developing a skilled workforce capable of managing and executing redevelopment projects effectively.
8. Political Instability and Policy Inconsistency
Political instability and policy inconsistency can disrupt urban redevelopment projects in Nigeria. Changes in government, shifts in policy priorities, and political interference can create uncertainties and delays in project implementation. Ensuring political support and stability, as well as maintaining consistent policies and regulations, is crucial for the successful execution of redevelopment initiatives.
Addressing the Challenges
To effectively address the challenges of urban redevelopment in Nigeria, a comprehensive and collaborative approach is necessary. Key strategies include:
1. Improving Urban Planning and Infrastructure: Enhancing urban planning practices and investing in infrastructure development can create a solid foundation for redevelopment projects. This includes updating zoning regulations, improving infrastructure networks, and adopting integrated planning approaches.
2. Streamlining Land Acquisition Processes: Reforming land tenure systems and addressing land ownership disputes can facilitate smoother land acquisition for redevelopment projects. Implementing transparent and efficient land registration processes is also essential.
3. Combating Corruption and Bureaucratic Inefficiencies: Strengthening anti-corruption measures and streamlining regulatory procedures can improve project efficiency and reduce delays. Promoting transparency and accountability in project management is critical.
4. Exploring Innovative Financing Solutions: Developing diverse financing options, including public-private partnerships and alternative funding mechanisms, can help secure the necessary capital for redevelopment projects.
5. Engaging Communities and Addressing Social Concerns: Involving communities in the planning process and providing support for displaced residents can help mitigate social resistance and ensure that redevelopment projects benefit local populations.
6. Promoting Environmental Sustainability: Integrating sustainable practices and technologies into redevelopment projects can minimize environmental impact and promote long-term sustainability.
7. Building Technical Capacity: Investing in training and capacity-building initiatives can enhance the technical expertise required for successful redevelopment projects.
8. Ensuring Political Stability and Policy Consistency: Maintaining political support and consistent policies can provide a stable environment for implementing redevelopment projects.
Conclusion
Urban redevelopment projects in Nigeria face a range of challenges, from inadequate infrastructure and land ownership issues to corruption and environmental concerns. Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated effort from government authorities, private sector stakeholders, and local communities. By implementing effective strategies and fostering collaboration, Nigeria can overcome these obstacles and achieve successful urban redevelopment that enhances the quality of life for its citizens and supports sustainable urban growth.
Urban Redevelopment
. Infrastructure Deficits
. Land Ownership Disputes
. Corruption and Bureaucracy
. Funding and Financial Constraints
. Social Displacement
. Environmental Sustainability
. Technical Expertise
. Policy Inconsistency
. Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Contact Us
Chaman Law Firm today. Our offices are conveniently located in Lagos, FCT Abuja, Ogun State, and the UK. We are readily available to assist you with your legal needs. Whether you require consultation, representation, or ongoing legal support, Chaman Law Firm is your trusted partner.
Call us at 08065553671 or email us at info@chamanlawfirm.com to schedule a consultation.

