Critical Legal Responsibilities of Corporate Boards and Executives: Ensuring Accountability and Success
Introduction
The legal responsibilities of corporate boards and executives are central to the success, integrity, and compliance of any business entity. Corporate boards and executives serve as the stewards of a company, entrusted with the task of guiding the organization to achieve its strategic goals while adhering to a legal and ethical framework. Understanding the legal responsibilities of corporate boards and executives is crucial for both the individuals occupying these positions and the stakeholders they serve. In many cases, failure to meet these responsibilities can lead to legal, financial, and reputational consequences.
Corporate governance plays a pivotal role in ensuring that companies are well-managed and aligned with the interests of shareholders, employees, and other stakeholders. The roles of corporate boards and executives in governance are defined by a combination of statutory requirements, regulatory expectations, and ethical considerations. This article provides an in-depth understanding of the legal responsibilities of corporate boards and executives, highlighting their importance and the consequences of non-compliance.
1. Corporate Governance and Legal Duties
At the heart of corporate governance are the legal duties owed by the board of directors and senior executives to the company and its stakeholders. These duties are designed to ensure that companies operate in an ethical, transparent, and accountable manner. The legal responsibilities of corporate boards and executives can be broadly categorized into three main areas: fiduciary duties, statutory obligations, and regulatory compliance.
a) Fiduciary Duties
Fiduciary duties are the most fundamental legal responsibilities of corporate boards and executives. These duties are owed to the company and its shareholders, and they are designed to ensure that corporate leaders act in the best interests of the company.
Duty of Care
: The duty of care requires corporate directors and executives to make informed and well-considered decisions when managing the affairs of the company. This duty mandates that board members and executives exercise a reasonable level of diligence, prudence, and competence when making decisions that impact the organization. This means reviewing relevant information, considering expert advice when necessary, and carefully evaluating the potential risks and rewards of any course of action.Duty of Loyalty
: The duty of loyalty obligates corporate boards and executives to act in the best interests of the company, putting the interests of the corporation above their own personal interests. This duty is designed to prevent conflicts of interest, self-dealing, and other unethical behavior that could harm the company or its stakeholders. Directors and executives must disclose any potential conflicts of interest and recuse themselves from decisions where their personal interests may conflict with the interests of the company.Duty of Good Faith
: This duty requires corporate directors and executives to act honestly and with integrity when managing the company. The duty of good faith encompasses both the duty of care and the duty of loyalty, ensuring that corporate leaders act in the company’s best interests and do not engage in fraudulent or dishonest conduct.
b) Statutory Obligations
In addition to fiduciary duties, corporate boards and executives are subject to various statutory obligations. These obligations are set out in corporate laws and regulations that govern how companies operate. In many jurisdictions, corporate statutes require boards and executives to adhere to certain governance standards and to fulfill specific responsibilities.
Compliance with Corporate Laws
: Corporate boards and executives must ensure that the company complies with all relevant laws and regulations, including the Companies and Allied Matters Act (CAMA) in Nigeria or the Companies Act in other jurisdictions. This includes complying with statutory requirements related to the incorporation, management, and dissolution of the company.Financial Reporting
: One of the most important statutory obligations of corporate boards and executives is ensuring accurate and transparent financial reporting. Public companies are required to disclose financial information to regulators, shareholders, and the public. This includes preparing and filing audited financial statements, annual reports, and other disclosures in accordance with applicable accounting standards. Failure to meet these obligations can result in penalties, fines, and damage to the company’s reputation.Shareholder Rights
: Corporate boards and executives must respect the rights of shareholders, including their right to participate in corporate decision-making through voting at general meetings, their right to receive dividends, and their right to access accurate information about the company’s performance. Boards must ensure that shareholders are treated fairly and equitably, particularly in matters such as mergers, acquisitions, and other major corporate transactions.
c) Regulatory Compliance
Beyond statutory obligations, corporate boards and executives are also responsible for ensuring that the company complies with all applicable regulatory requirements. Regulatory compliance is especially important in industries that are heavily regulated, such as banking, finance, healthcare, and energy.
Sector-Specific Regulations
: Corporate boards and executives must ensure that the company complies with all industry-specific regulations. For example, companies in the financial sector must adhere to regulations set by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and other regulatory authorities. Compliance with environmental laws, labor laws, and consumer protection regulations is also critical.Corporate Governance Codes
: Many countries, including Nigeria, have introduced corporate governance codes that provide guidance on best practices for boards and executives. While these codes may not always have the force of law, they are considered an important part of regulatory compliance. Companies that fail to adhere to corporate governance codes may face scrutiny from regulators, shareholders, and the media.
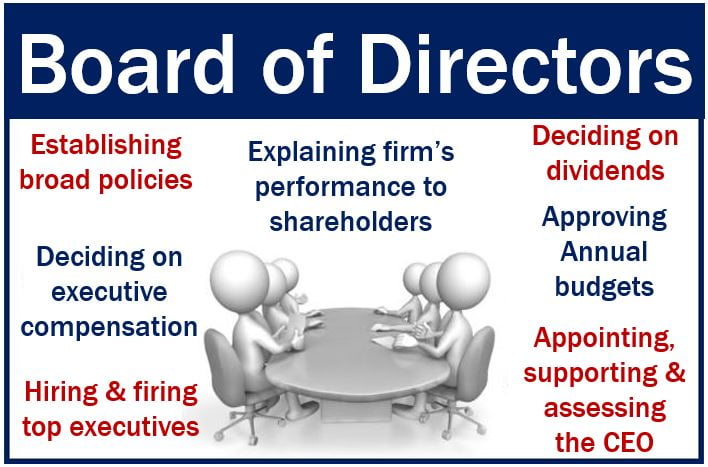
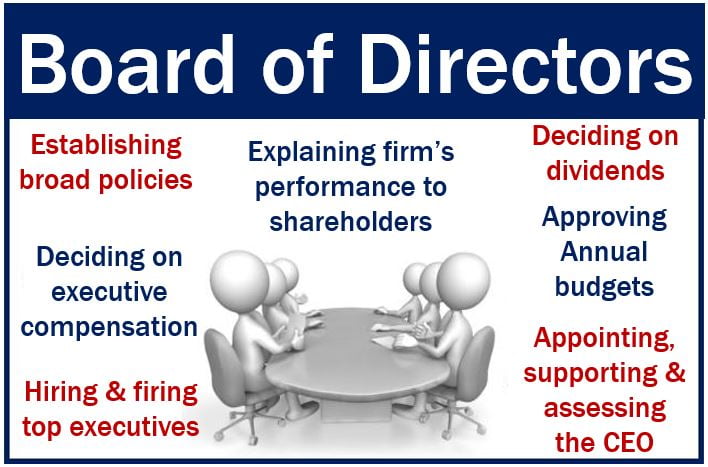
2. Responsibilities of the Board of Directors
The board of directors is the highest decision-making body in a company, responsible for overseeing the management of the business and ensuring that it is run in a manner that benefits the shareholders. The board’s key responsibilities include:
a) Strategic Oversight
The board is responsible for setting the company’s long-term strategy and ensuring that it aligns with the company’s goals and objectives. This includes approving major business decisions, such as mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures, as well as setting the company’s risk appetite.
b) Monitoring Management
The board must oversee the performance of senior executives and ensure that the company’s management is acting in the best interests of the company. This includes evaluating the performance of the CEO and other top executives and ensuring that they are held accountable for their decisions.
c) Ensuring Ethical Conduct
The board is responsible for promoting ethical behavior within the company. This includes setting the tone at the top by establishing a strong corporate culture based on integrity, transparency, and accountability. The board must also ensure that the company has a code of conduct in place and that employees and executives adhere to it.
d) Risk Management
Corporate boards are responsible for overseeing the company’s risk management processes. This includes identifying potential risks to the business, assessing their impact, and ensuring that the company has appropriate controls in place to mitigate them. The board’s risk management responsibilities are particularly important in industries that are exposed to significant financial, operational, or regulatory risks.
3. Responsibilities of Corporate Executives
Corporate executives, including the CEO, CFO, and other senior managers, are responsible for the day-to-day operations of the company. Their legal responsibilities include:
a) Implementing the Board’s Strategy
Executives are responsible for implementing the strategic decisions made by the board of directors. This includes executing business plans, managing resources, and ensuring that the company meets its operational targets.
b) Managing Corporate Resources
Corporate executives are responsible for managing the company’s resources efficiently. This includes overseeing the company’s finances, assets, and human resources. Executives must ensure that resources are used in a way that maximizes shareholder value while minimizing waste and inefficiency.
c) Maintaining Compliance
Executives must ensure that the company complies with all legal and regulatory requirements. This includes staying up to date with changes in the law and ensuring that the company’s policies and procedures are in line with regulatory expectations.
4. Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to meet the legal responsibilities of corporate boards and executives can have serious consequences for both the individuals involved and the company as a whole. These consequences may include:
Legal Liability
: Corporate boards and executives may be held personally liable for breaches of fiduciary duties or violations of statutory obligations. This can result in civil lawsuits, fines, and penalties.Reputational Damage
: Companies that fail to comply with corporate governance standards or regulatory requirements may suffer damage to their reputation, leading to a loss of investor confidence and customer trust.Financial Losses
: Non-compliance with legal and regulatory requirements can result in significant financial losses for the company, including fines, penalties, and legal costs.
Conclusion
Having examined the critical legal responsibilities of corporate boards and executives, it becomes abundantly clear that the modern-day corporate leader is not merely a figurehead of strategy or vision. They are legal stewards of the business enterprise, entrusted with the duty to uphold laws, act ethically, and promote good governance. In Nigeria and globally, the evolving landscape of corporate law demands more than strategic insight—it requires a legally aware and ethically committed leadership. Fulfilling these legal responsibilities is not an optional add-on to effective leadership; it is the foundation upon which all corporate success must rest.
Boards and executives must recognize that their roles are governed by a matrix of statutory provisions, judicial decisions, and evolving best practices. Compliance with these legal requirements is no longer the sole domain of the company secretary or legal department—it must be integrated into every facet of boardroom conduct and executive decision-making. Directors who fail to observe their legal duties may be held personally liable, with consequences ranging from financial penalties to criminal sanctions and disqualification from future corporate roles. Moreover, legal breaches can erode stakeholder trust and inflict long-lasting reputational damage that no amount of financial recovery can repair.
There is immense value in compliance. Boards and executives that embrace their legal responsibilities foster transparency, encourage stakeholder engagement, and build reputational capital that positions the company for long-term success. Investors are increasingly inclined to commit capital to companies with strong governance track records. Regulators are more likely to work cooperatively with organizations that demonstrate a proactive commitment to legal compliance. Even consumers, especially in the digital age, favor brands that demonstrate ethical leadership and legal accountability.
Failure to act, on the other hand, is a silent but deadly risk. The law punishes not just deliberate misconduct but also negligence and omission. Directors who turn a blind eye to regulatory breaches or financial misreporting may find themselves ensnared in legal proceedings regardless of their intent. Legal responsibility includes the duty to ask tough questions, challenge management when necessary, and demand transparency in financial and operational reporting. It is not enough to claim ignorance or rely on others; each board member and executive must individually and collectively ensure the company is acting within the bounds of the law.
The case law is replete with examples where directors and executives were held accountable for governance failures. In Nigerian jurisprudence, courts have reiterated that a board member’s duty is not extinguished by delegation or silence. In Okeowo v. Migliore, the court emphasized the fiduciary nature of a director’s role and the corresponding obligation to act with utmost honesty and fairness. Such judgments are a wake-up call for corporate leaders who might otherwise assume their role is ceremonial or advisory in nature.
The pathway to legal compliance and ethical leadership is not without its challenges, but it is certainly attainable. Boards and executives must institutionalize continuous legal education, conduct periodic governance reviews, and build robust compliance frameworks. This means actively engaging with legal counsel, implementing whistleblower mechanisms, and fostering a corporate culture that values integrity and accountability. Transparency must become a core value, not just a regulatory obligation.
Leadership also demands courage—the courage to act decisively in the face of wrongdoing, to report misconduct when observed, and to resign from positions where legal or ethical compromise becomes inevitable. A company’s tone is set at the top, and when the board and executives lead by example, the rest of the organization is more likely to follow. Conversely, when leaders cut corners, the ripple effect of misconduct can cascade downwards, infecting every layer of the enterprise.
As corporate entities expand into global markets and embrace digital transformation, the responsibilities of boards and executives will continue to grow in complexity. Issues such as cybersecurity, data protection, environmental compliance, and ESG reporting are now squarely within the purview of corporate leadership. This evolution calls for an agile, informed, and forward-looking approach to legal compliance.
Ultimately, the legal responsibilities of corporate boards and executives are not hurdles but guides. They illuminate the path toward sustainable business practices, equitable treatment of stakeholders, and institutional trustworthiness. Companies that internalize these responsibilities as core to their operations are better positioned to withstand crises, attract investment, and deliver long-term value.
Corporate governance is not static; it is a dynamic process that requires regular reflection and adaptation. Boards and executives who rise to the occasion—who see their legal duties not as burdens but as the pillars of credible leadership—will not only ensure compliance but also inspire a new standard of excellence in corporate Nigeria and beyond. In doing so, they will build not just profitable organizations, but principled ones—businesses that endure, succeed, and lead with integrity.
In conclusion, the legal responsibilities of corporate boards and executives are critical to the success and sustainability of a company. By understanding and adhering to these responsibilities, corporate leaders can ensure that their companies operate in an ethical, transparent, and compliant manner, ultimately benefiting all stakeholders.
Contact Us
For premier legal research services in Corporate law cases in Nigeria, contact Chaman Law Firm today. Our offices are conveniently located in Lagos, FCT Abuja, Ogun State, and the UK. We are readily available to assist you with your legal needs. Whether you require consultation, representation, or ongoing legal support, Chaman Law Firm is your trusted partner in navigating Corporate law in Nigeria.
Call us at 08065553671 or email us at info@chamanlawfirm.com to schedule a consultation.
- Corporate Governance
- Mergers and Acquisitions
- Insolvency and Restructuring
- Securities Law
- Corporate Finance
Chaman Law Firm: Your Trusted Legal Partner in Corporate Law
By choosing Chaman Law Firm, you are selecting a team of dedicated professionals committed to providing exceptional legal services tailored to your unique needs. Let us be your advocate and guide in the complex world of Corporate law, ensuring your interests are protected and your goals are achieved.